2024.04.15 Monday
Green-to-Red Transformation of Euglena gracilis Using Bonito Stock and Intense Red Light
Scientists explore a simple and sustainable method to increase the growth and carotenoid content ratio of an edible microalga
Over the past few years, people have generally become more conscious about the food they consume. Thanks to easier access to information as well as public health campaigns and media coverage, people are more aware of how nutrition ties in with both health benefits and chronic diseases. As a result, there is an ongoing cultural shift in most countries, with people prioritizing eating healthily. In turn, the demand for healthier food options and nutritional supplements is steadily growing.
In line with these changes, Assistant Professor Kyohei Yamashita from Tokyo University of Science (TUS), Japan, has been studying a promising "superfood" called Euglena gracilis for over half a decade. A species of edible microalgae, E. gracilis has a rich nutritional profile, with a unique combination of vitamins, fibers, lipids, and proteins. Like most other photosynthetic plants, E. gracilis also contains carotenoids—natural substances with a wide variety of health benefits.
In a study published in 2023, a research team from TUS found a simple method to efficiently grow E. gracilis in an inexpensive medium (solid or liquid that contains nutrients and is used to grow bacteria) based on tomato juice. Now, in a new study, the researchers have explored a promising technique to make cultured E. gracilis produce carotenoids at a higher rate, rendering it even more nutritious. This study, which was co-authored by Dr. Kengo Suzuki from Euglena Co., Ltd., as well as Professor Tatsuya Tomo and Professor Eiji Tokunaga from TUS, was published in Volume 13, Issue 4 of the journal Plants in February 12, 2024.
The proposed approach is quite straightforward, and so is its rationale. When a plant is exposed to high-intensity light for extended periods of time, it undergoes a light-stress response. This, in turn, can cause the organism to produce molecules that protect it from further light exposure, including carotenoids. Based on these facts, the researchers investigated whether they could induce such a reaction in E. gracilis to enhance its carotenoid content ratio.
To this end, the team ran a series of experiments on multiple batches of cultured E. gracilis. They exposed cultures to light of different wavelengths (or colors) and at different intensities looking for a "reddening reaction," which is a tell-tale sign of higher carotenoid production in many plant species. Moreover, they also tested a new culture medium based on bonito stock, a soup stock extracted from Katsuobushi, a traditional Japanese dish made from smoked bonito fish.
Interestingly, the researchers found that strong red-light irradiation at 605–660 nm triggered a reddening reaction in E. gracilis when cultured in bonito stock. They also looked at the chemical profiles of the cultures using high-performance liquid chromatography, both at the culture and single-cell level. These analyses revealed that reddened cells not only had a high concentration of diadinoxanthin, the most abundant carotenoid in E. gracilis, but also produced an unidentified xanthophyll-type carotenoid. On top of these, the team also noted that bonito stock cultures grew quicker and reached higher densities than cultures grown on conventional media, and likely produced more types or amounts of carotenoids.
Together, the results of this study could pave the way for an innovative and easily scalable technique for growing nutritious E. gracilis. The method's simplicity is certainly one of its strengths, as Dr. Yamashita remarks, "Our approach does not involve genetic modifications and could thus be readily adopted by the food industry to expand the use of E. gracilis, both in food and as a nutritional supplement." Notably, bonito stock is a nutritious food and using it in the culture medium would, therefore, provide additional health benefits.
Aside from its benefits to us humans, growing E. gracilis can also help the environment. "E. gracilis cultivation, which requires relatively few resources, can be a sustainable food resource," explains Dr. Yamashita. "Our research marks an important step toward the development of new food technologies that contribute to people's lives from both health and environmental perspectives."
With the carotenoid market poised to become a multi-billion-dollar industry by 2030, this study will help deepen our understanding of carotenoid biosynthetic pathways, hopefully leading to the development of sustainable practices in the production of nutritional supplements and emerging foods.

Image title: Effect of light intensity on E. gracilis cultured in conventional medium and bonito stock medium
Image caption: The researchers discovered that strong red-light irradiation triggered a reddening reaction in E. gracilis when cultured in bonito stock medium. This indicates that the carotenoids are present at a higher rate and are diverse. Thus, the use of bonito stock medium to culture E. gracilis can help develop a more nutritious food source.
Image credit: Dr. Kyohei Yamashita from TUS, Japan
License type: Original content
Usage restrictions: Cannot be reused without permission
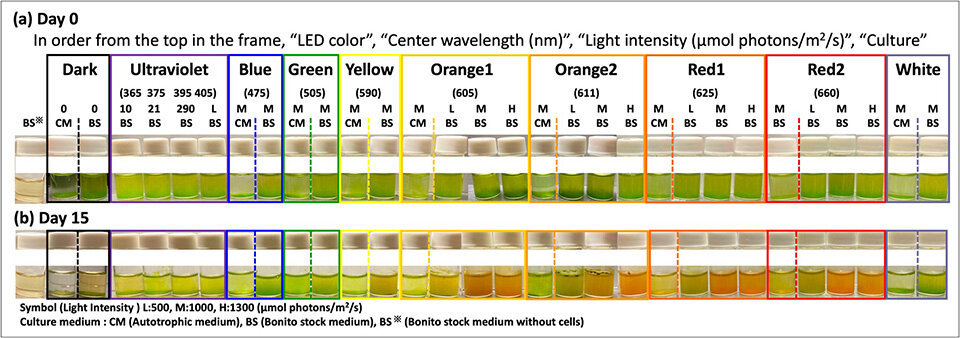
Image title: Effect of wavelength and light intensity on cell reddening in Cramer–Myers and bonito stock medium
Image caption: The number of days elapsed excludes the pre-cultivation period (6 days). Marked culture reddening was observed in samples of bonito stock medium irradiated with warm-colored light-emitting diodes (Orange 1,2 and red 1, 2).
Image credit: Dr. Kyohei Yamashita from TUS, Japan
License type: Original content
Usage restrictions: Cannot be reused without permission
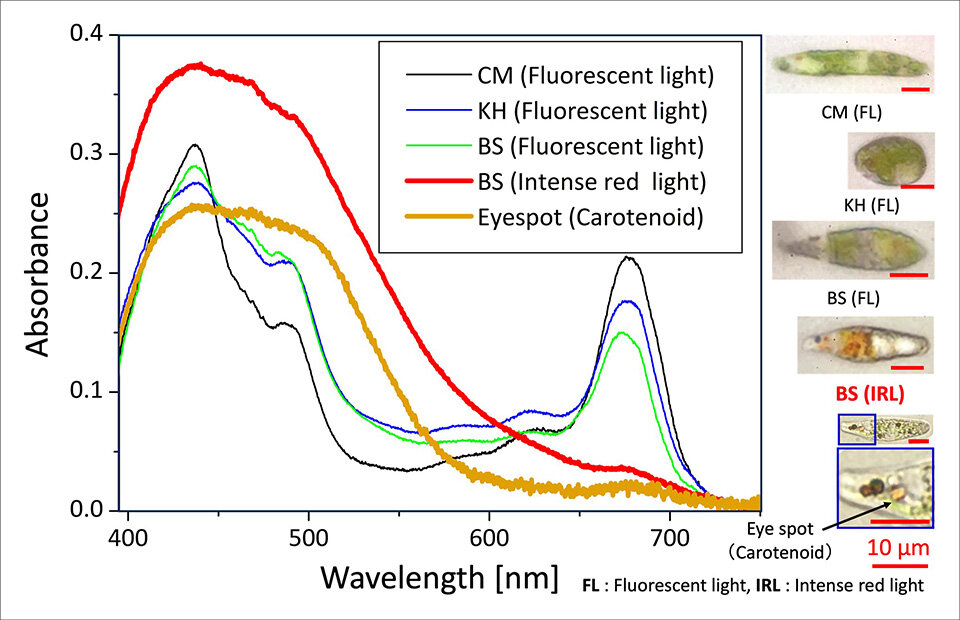
Image title: Absorption spectra of single cells
Image caption: The absorption spectrum of the reddened cells showed a similarity to that of the eyespot, which predominantly contains carotenoids.
Image credit: Dr. Kyohei Yamashita from TUS, Japan
License type: Original content
Usage restrictions: Cannot be reused without permission
Reference
| Title of original paper | : | Reddening of the Unicellular Green Alga Euglena gracilis by Dried Bonito Stock and Intense Red Light Irradiation |
| Journal | : | Plants |
| DOI | : | 10.3390/plants13040510 |
| Authors | : | Kyohei Yamashita1, Ryusei Hanaki2, Ayaka Mori1, Kengo Suzuki3, Tatsuya Tomo2, and Eiji Tokunaga1 |
| Affiliations | : |
1Department of Physics, Faculty of Science Division I, Tokyo University of Science 2Graduate School of Science, Tokyo University of Science 3Euglena Co., Ltd. |
About The Tokyo University of Science
Tokyo University of Science (TUS) is a well-known and respected university, and the largest science-specialized private research university in Japan, with four campuses in central Tokyo and its suburbs and in Hokkaido. Established in 1881, the university has continually contributed to Japan's development in science through inculcating the love for science in researchers, technicians, and educators.
With a mission of "Creating science and technology for the harmonious development of nature, human beings, and society," TUS has undertaken a wide range of research from basic to applied science. TUS has embraced a multidisciplinary approach to research and undertaken intensive study in some of today's most vital fields. TUS is a meritocracy where the best in science is recognized and nurtured. It is the only private university in Japan that has produced a Nobel Prize winner and the only private university in Asia to produce Nobel Prize winners within the natural sciences field.
■
Tokyo University of Science(About TUS)

About Assistant Professor
Kyohei Yamashita
from Tokyo University of Science
About Professor
Eiji Tokunaga
from Tokyo University of Science
About Professor
Tatsuya Tomo
from Tokyo University of Science
Funding information
This research was supported by JSPS KAKENHI grant No. 21K06101.

