2021.08.30 Monday
Hidden in the Seeds: Bacteria Found to Survive the Harsh Interior of Passion Fruit Seeds
Scientists discover endophytic bacteria that can survive the unfavorable interior of passion fruit seeds and get transmitted to the seedlings on germination
Plant endophytic microorganisms, especially those growing inside seeds, can survive antimicrobial compounds and have attracted attention for their potential biocatalytic activity. Recently, researchers from Japan successfully isolated several strains of endophytic bacteria that survive in high concentrations of antimicrobial resveratrol and piceatannol inside passion fruit seeds and get transmitted to next-generation seedlings. One of the bacteria could convert resveratrol and piceatannol to their respective derivatives. These findings will significantly advance endophyte and biocatalyst research.
 |
Similar to the well-known human gut-resident microbes, the inside of a plant can also shelter microorganisms. Residing inside roots, stems, leaves, fruits, and even seeds, and developing a synergistic relationship with their host, these 'endophytic' microorganisms need not necessarily harm the plant. Instead, they are often beneficial in germination, growth, and defense. However, plant interiors also contain many "secondary metabolites", which are natural bioactive compounds that have strong antimicrobial properties, making this environment typically hostile for microorganisms.
Now, for the first time ever, a research group consisting of Dr. Toshiki Furuya, Associate Professor at the Department of Applied Biological Science, Tokyo University of Science, Japan, has succeeded in isolating bacteria from the seeds of passion fruit (Passiflora edulis). Their research, which also unearths the surviving mechanisms of these bacteria inside the seeds, has been published in the journal MicrobiologyOpen.
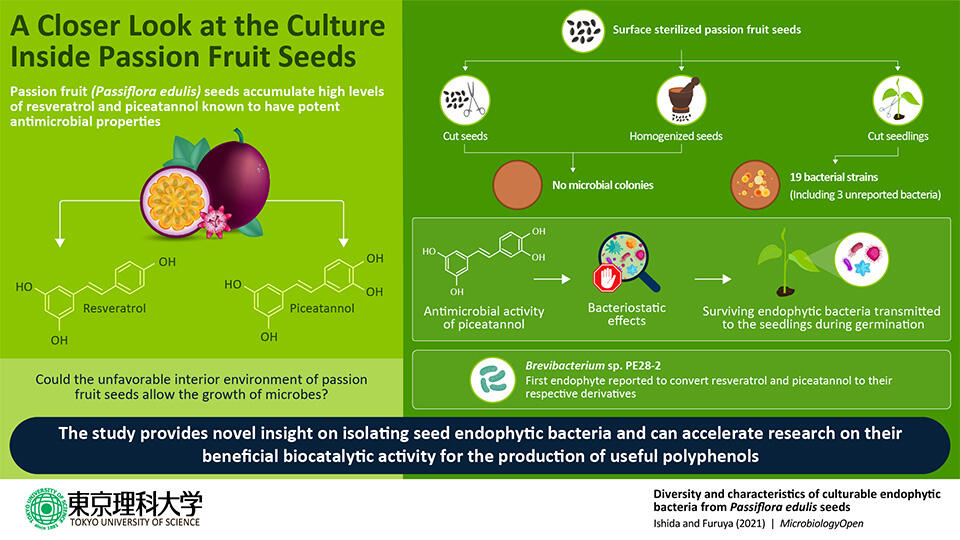
In their study, the scientists focused on the seeds of P. edulis. The seeds of this fruit are full of secondary metabolites with strong antimicrobial properties, such as resveratrol and piceatannol—the latter present at high levels of up to 2.2 mg/g. As Dr. Furuya reveals the rationale behind choosing passion fruit seeds for the study, "The extraordinarily high concentration of piceatannol protects P. edulis seeds from microorganisms. We thought it would be interesting to know if any endophytic microorganism could survive this extreme environment, and if yes, how." Earlier reports showed that endophytes capable of surviving in an environment rich in biologically active compounds possessed biocatalytic activities related to the metabolism of these compounds. The fact that their biocatalytic potential could be exploited for therapeutic purposes made the scientists even more eager to explore the presence of endophytic bacteria.
The scientists collected and surface-sterilized the seeds of naturally grown P. edulis before either cutting or crushing them and placing them on solid agar-based growth media to check for microbial growth. While no microbial colony appeared from the cut or homogenized seeds, interestingly, the seedlings sprouting from the cut seeds, when exposed to growth media, gave rise to microbial colonies. The scientists then performed sequencing to identify the bacteria that appeared on the agar plate.
The findings were remarkable. From the seedlings, the scientists isolated 19 strains, including three previously unreported strains of bacteria from various genera. They hypothesized that inside the seeds, piceatannol exerted bacteriostatic (or "bacterial growth-stalling") rather than bactericidal (or "bacteria-killing") effects on the residing bacteria. Ms. Aoi Ishida, the co-author of the study explains: "Due to the presence of a high concentration of piceatannol, the growth of the bacteria was stagnated inside the seed, but when transmitted to the next-generation seedlings during germination, the bacteria were relieved from the effect of piceatannol and able to grow again." The scientists also found one of the bacteria, Brevibacterium sp. PE28-2, to possess the ability to convert resveratrol and piceatannol to their respective derivatives. This is the first endophyte shown to exhibit such activity.
Dr. Furuya and Ms. Ishida are very hopeful that the method established in this study is expected to be effective in isolating several useful endophytic bacteria from a variety of plants. Moreover, considering the current focus on engineering new biomolecules with diverse applications, the results of this study would accelerate research on seed endophytic bacteria.
Reference
| Title of original paper | : | Diversity and characteristics of culturable endophytic bacteria from Passiflora edulis seeds |
| Journal | : | MicrobiologyOpen |
| DOI | : | 10.1002/mbo3.1226 |
About The Tokyo University of Science
Tokyo University of Science (TUS) is a well-known and respected university, and the largest science-specialized private research university in Japan, with four campuses in central Tokyo and its suburbs and in Hokkaido. Established in 1881, the university has continually contributed to Japan's development in science through inculcating the love for science in researchers, technicians, and educators.
With a mission of "Creating science and technology for the harmonious development of nature, human beings, and society", TUS has undertaken a wide range of research from basic to applied science. TUS has embraced a multidisciplinary approach to research and undertaken intensive study in some of today's most vital fields. TUS is a meritocracy where the best in science is recognized and nurtured. It is the only private university in Japan that has produced a Nobel Prize winner and the only private university in Asia to produce Nobel Prize winners within the natural sciences field.
About Dr. Toshiki Furuya from Tokyo University of Science
Dr. Toshiki Furuya is an Associate Professor at the Department of Applied Biological Science, Tokyo University of Science, Japan. He received his PhD degree from Waseda University Graduate School, Division of Science and Engineering Department of Applied Chemistry. His research interests lie in the field of biotechnology, spanning over topics such as endophyte, microbial metabolism, enzyme catalysis, bioproduction, and bioremediation. He has received several prestigious awards, including the Mizuno Award, the Award for Researches on Enzyme Engineering, and the 24th Excellent Paper Award, Society of Biotechnology, Japan, among others. He has published more than 35 research papers in reputed journals.
https://www.tus.ac.jp/en/fac/p/index.php?6D15 

