2021.03.24 Wednesday
Quantitative Detection of Fatty Liver Disease by Assessing Fat Distribution in the Liver
A noninvasive method for quantifying fat content in liver can aid medical research and diagnosis of liver diseases
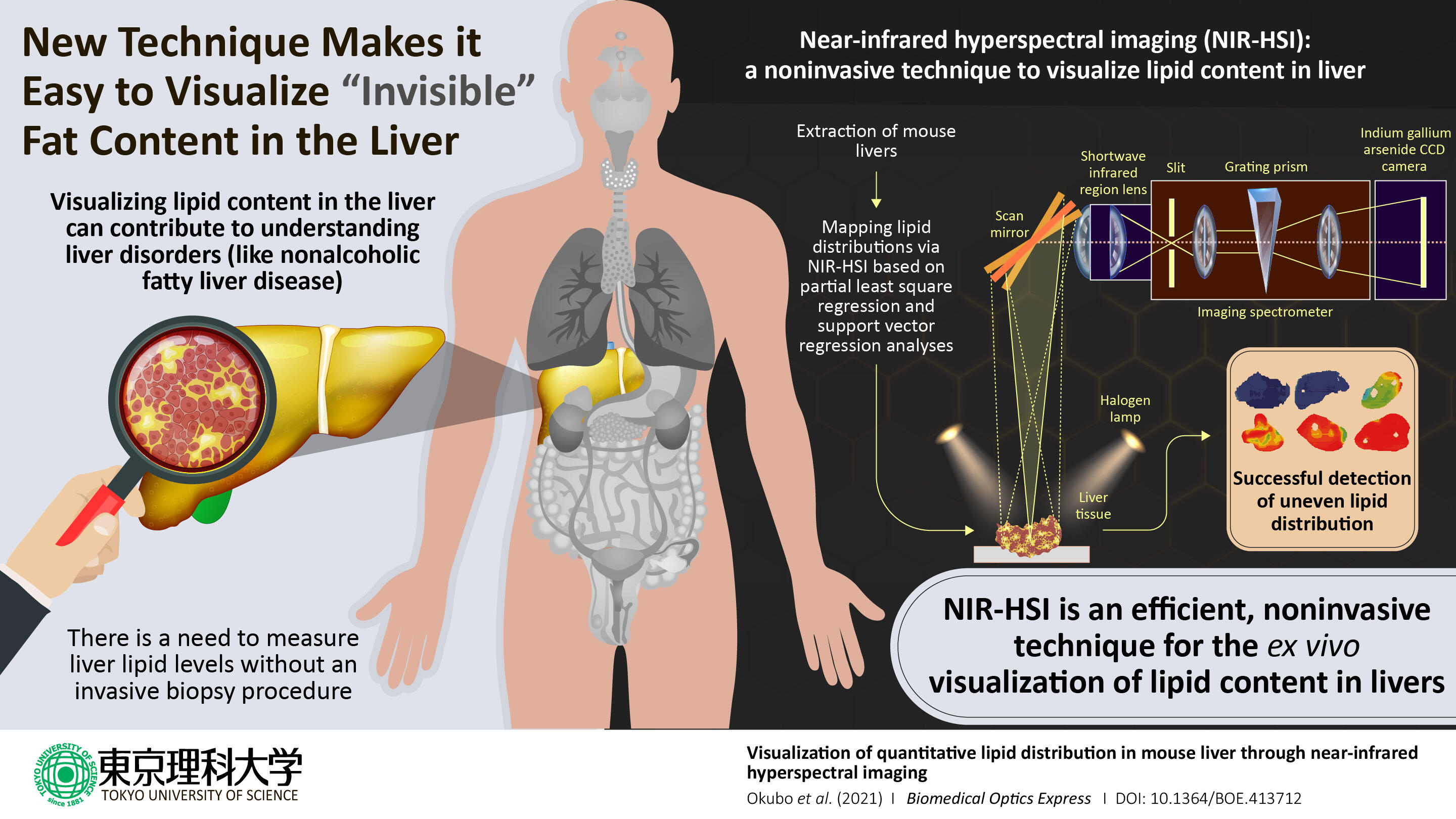
Excessive fat accumulation in the liver can lead to serious medical problems, including liver failure. Thus, understanding the distribution of lipids within the liver is a critical step in diagnosing fatty liver diseases. A team of researchers at Tokyo University of Science has now shown that near-infrared hyperspectral imaging permits the visualization of lipid content in mouse liver. This technique can facilitate the diagnosis of fatty liver diseases in medical research.
 |
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a pathological condition characterized by excessive fat stored in the liver that is not attributed to heavy alcohol consumption, which can lead to liver failure and even cancer. Obesity, type 2 diabetes, and high cholesterol levels are all risk factors for this disease, and like the global prevalence of obesity, the prevalence of NAFLD is coincidently expected to rise as well.
It is therefore critical for clinicians to handle effective tools for diagnosing NAFLD. The current standard method for diagnosis is analysis of liver biopsy samples. However, this approach has shortcomings such as invasiveness and the potential for sampling errors, so there is a pressing need for reliable noninvasive methods. In a new study published in the journal Biomedical Optics Express, a team of researchers, led by Professor Kohei Soga of Tokyo University of Science including Assistant Professor Kyohei Okubo of Tokyo University of Science and Professor Naoko Ohtani of Osaka City University, reports the successful use of near-infrared hyperspectral imaging to quantitatively analyze the distributions of lipids (a class of lipids commonly found in fat) in mouse liver. Dr. Okubo says, "Lipid distribution in the liver provides crucial information for diagnosing fatty liver-associated liver diseases including cancer, and therefore, a noninvasive, label-free, quantitative modality is needed."
In describing the inspiration for this project, Dr. Okubo collaborated with Professor Ohtani, who studies the relationship between obesity and liver disease. Given the success of other research groups in using near-infrared hyperspectral imaging to visualize plaques in rabbit blood vessels and fatty acids in pork meats, Prof. Soga's team decided to try using it to visualize the distribution of lipids in mouse liver.
The study focused on mice that were either on a normal diet or one of three kinds of high-fat diets rich in various types of lipids. The objective of these varied diets was to generate a set of livers with diverse lipid profiles. After extracting the livers, the scientists used a reference test to generate convincing results for comparing their hyperspectral imaging results. They used the Folch extraction method to isolate lipids from small pieces of the livers and then weighed the isolated lipid samples to calculate the total weight of lipids within the livers. The scientists next performed near-infrared hyperspectral imaging and used two candidate data analysis methods―partial least-square regression and support vector regression―to quantitatively visualize lipid distributions within the liver to identify the better analytical method.
When the scientists examined their data, they found that it enabled them to image the livers in gradient colors according to the lipid levels contained in the livers and to generate maps of the local lipid densities within the livers. The lipid levels as measured with hyperspectral imaging closely correlated with the actual lipid levels as quantified based on Folch extraction method, and this correlation was stronger in the lipid levels calculated using support vector regression than for the lipid levels calculated using partial least square regression.
In articulating the significance of his team's research, Dr. Okubo notes, "We have developed a method to visualize the distribution of lipids in the liver using a near-infrared spectral imaging technique that incorporates machine learning." This is important because near-infrared spectral imaging technologies could be used for the noninvasive evaluation of the liver status, thus providing a diagnostic option for clinicians when investigating NAFLD cases. Near-infrared spectral imaging can also be used to detect specific lipid compound types, and Dr. Okubo is quick to emphasize that "the ultimate goal of this collaborative research is to differentiate and identify fatty acids in the liver." Achieving this future goal would represent a major advancement in research in fatty liver diseases.
Reference
| Title of original paper | : | Visualization of quantitative lipid distribution in mouse liver through near-infrared hyperspectral imaging |
| Journal | : | Biomedical Optics Express |
| DOI | : | 10.1364/BOE.413712 |
About The Tokyo University of Science

Tokyo University of Science (TUS) is a well-known and respected university, and the largest science-specialized private research university in Japan, with four campuses in central Tokyo and its suburbs and in Hokkaido. Established in 1881, the university has continually contributed to Japan's development in science through inculcating the love for science in researchers, technicians, and educators.
With a mission of "Creating science and technology for the harmonious development of nature, human beings, and society", TUS has undertaken a wide range of research from basic to applied science. TUS has embraced a multidisciplinary approach to research and undertaken intensive study in some of today's most vital fields. TUS is a meritocracy where the best in science is recognized and nurtured. It is the only private university in Japan that has produced a Nobel Prize winner and the only private university in Asia to produce Nobel Prize winners within the natural sciences field.
About Dr. Kyohei Okubo from Tokyo University of Science
Kyohei Okubo, PhD, is an Assistant Professor at Tokyo University of Science. He completed his undergraduate and postgraduate education at University of Tsukuba, and he has worked at the University of Tokyo and Innovation Center of NanoMedicine (iCONM), Japan. He has conducted research into photonic sensors, the fabrication of nanoplasmonic devices, nanoarray chips, and near-infrared bioimaging. He has authored 28 publications.
PROFILE
Okubo Kyohei Assistant Professor
https://www.tus.ac.jp/en/fac/p/index.php?7086 
About Professor Kohei Soga from Tokyo University of Science
Kohei Soga, PhD, is a Professor at Tokyo University of Science. He completed his undergraduate and postgraduate education at the University of Tokyo. He has been focusing his research on the interdisciplinary fields of bio- and nano-photonics, with the aim to develop a biophotonic system with near-infrared excitation.
PROFILE
SOGA Kohei Professor
https://www.tus.ac.jp/en/fac/p/index.php?440b 
About Professor Naoko Ohtani from Osaka City Universit
Naoko Ohtani, MD, PhD, is a Professor at Osaka City University. She completed her undergraduate and postgraduate education at Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine. She has been investigating the mechanism of cancer development, particularly of obesity-associated liver cancer, focusing on the tumor microenvironment and involvement of gut microbiota in liver diseases.
Funding information
This study was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, and the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.

